Disclosure
This website is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program,
an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees
by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
Understanding LiFePO4 battery voltage is critical for performance and longevity. This complete guide provides the essential voltage charts you need. We cover 12V, 24V, and 48V systems in detail.
Correct voltage monitoring prevents damage and maximizes battery life. It ensures your solar, RV, or marine system runs reliably. Avoid costly mistakes with precise data.
Best LiFePO4 Battery Chargers for Voltage Monitoring
Pairing your LiFePO4 battery with a compatible, smart charger is essential for maintaining optimal voltage. The right charger ensures precise charging cycles and prolongs battery life. Here are three top-rated chargers designed specifically for lithium iron phosphate chemistry.
Victron Energy Blue Smart IP65 Charger – Best Overall
The Victron Energy Blue Smart 12V 15A charger is a top-tier choice for its reliability and advanced features. It offers a dedicated LiFePO4 charging profile with adaptive multi-stage charging. Its Bluetooth connectivity allows for easy voltage monitoring and customization via a smartphone app. This model is ideal for RVs, marine applications, and critical backup systems.
NOCO Genius GENPRO10X1 – Best Value & Versatility
The NOCO Genius GENPRO10X1 10A charger delivers exceptional value with its support for multiple battery types, including LiFePO4. It features a force mode for recovering deeply discharged batteries and offers spark-proof technology. Its compact, rugged design makes it a perfect, portable solution for maintaining 12V batteries in cars, motorcycles, and power sports vehicles.
Renogy 40A DC-DC Charger – Best for Solar & Dual-Battery Systems
For mobile off-grid systems, the Renogy DCC50S 12V 50A DC-DC Charger with MPPT is the best option. It intelligently manages input from both a vehicle alternator and solar panels to safely charge your LiFePO4 bank. This all-in-one unit protects against overvoltage and is ideal for campervans, overland vehicles, and boats requiring integrated power management.
LiFePO4 Voltage Fundamentals
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries have a unique voltage profile distinct from lead-acid or other lithium types. Their stable discharge voltage is a key advantage. Understanding this profile is essential for accurate state-of-charge (SOC) monitoring and system design.
Nominal Voltage vs. Actual Voltage
The nominal voltage is a reference point, not the actual constant voltage. A 12V LiFePO4 battery has a nominal voltage of 12.8V. Its actual voltage fluctuates between approximately 10V and 14.6V during use. This range is much flatter than lead-acid, providing consistent power.
- Nominal Voltage: A standardized reference (e.g., 12.8V, 25.6V, 51.2V).
- Charging Voltage: The higher voltage applied during absorption (e.g., 14.2V-14.6V for 12V).
- Resting Voltage: The stable voltage after charging or discharging stops, used for accurate SOC reading.
Key Voltage Parameters and Their Meaning
Several specific voltage points define a LiFePO4 battery’s operation and limits. Knowing these prevents damage and maximizes cycle life. They are critical for setting your charge controller and inverter parameters correctly.
Key Takeaway: The most important voltages to know are the Full Charge (14.6V), 100% SOC Resting (13.3-13.4V), and Low Voltage Disconnect (10V-12V). Always program your equipment within the manufacturer’s specified range.
The table below outlines the critical voltage thresholds for a standard 12V LiFePO4 battery:
| Voltage Parameter | Typical Voltage (12V System) | Purpose & Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Full Charge (Absorption) | 14.2V – 14.6V | Top-off voltage; where charging current tapers. |
| Float/Storage Voltage | 13.5V – 13.8V | Maintenance voltage for long-term full charge. |
| 100% SOC (Resting) | 13.3V – 13.4V | True “full” voltage 1-2 hours after charge stops. |
| Low Voltage Disconnect (LVD) | ~12.0V | Protective cutoff to prevent deep discharge damage. |
LiFePO4 Voltage Chart: 12V, 24V, and 48V State of Charge
This section provides the essential voltage charts for common LiFePO4 battery configurations. Use these charts to accurately gauge your battery’s state of charge (SOC). Remember, voltage readings are most accurate when the battery is at rest.
(At Rest, ~25°C, no load or charging)
| State of Charge (%) | 12V LiFePO₄ | 24V LiFePO₄ | 48V LiFePO₄ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% | 13.5 V | 27.0 V | 54.0 V |
| 90% | 13.3 V | 26.6 V | 53.2 V |
| 80% | 13.25 V | 26.5 V | 53.0 V |
| 70% | 13.2 V | 26.4 V | 52.8 V |
| 60% | 13.15 V | 26.3 V | 52.6 V |
| 50% | 13.1 V | 26.2 V | 52.4 V |
| 40% | 13.05 V | 26.1 V | 52.2 V |
| 30% | 13.0 V | 26.0 V | 52.0 V |
| 20% | 12.9 V | 25.8 V | 51.6 V |
| 10% | 12.8 V | 25.6 V | 51.2 V |
Note: Voltage stays flat from ~80% to ~30% SOC — this is normal for LiFePO₄.
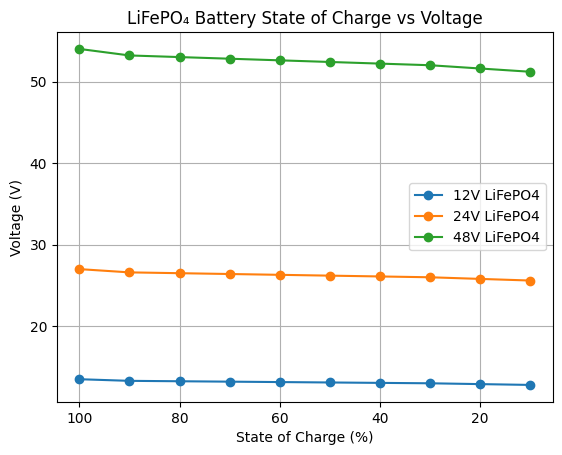
State of Charge Graph (Voltage vs SOC)
The graph above visually shows:
- Three flat curves (12V, 24V, 48V)
- Minimal voltage change across most of the SOC range
- Why voltage alone is unreliable for LiFePO₄ SOC estimation
Key insight from the graph:
- A battery at 13.2V (12V system) could be 70% or 40%
- Rapid voltage drop only occurs below ~20% SOC
Practical Takeaways
- Voltage charts are reference tools, not precision gauges
- Always rely on:
- BMS data
- Ah-based battery monitors
- Best operating range for longevity: 20% – 90% SOC
How to Maintain Optimal LiFePO4 Battery Voltage
Proper maintenance ensures your LiFePO4 battery performs reliably for thousands of cycles. Voltage management is the cornerstone of this longevity. Follow these proven practices to keep your battery within its ideal voltage range.
Correct Charging Practices for Longevity
Using the right charger settings is non-negotiable for LiFePO4 health. Incorrect voltage can cause stress and reduce lifespan. Always program your charger or solar charge controller to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Set Absorption Voltage: Program your charger to the correct absorption voltage, typically between 14.2V and 14.6V for a 12V system.
- Use a Dedicated Float: If using a float stage, set it between 13.5V-13.8V. Many experts recommend disabling float for storage and using a periodic top-up instead.
- Enable Low-Temp Charging Protection: Never charge a LiFePO4 battery below 32°F (0°C) without a built-in or external temperature sensor to prevent damage.
Monitoring and Balancing Your Battery Bank
Regular monitoring prevents small issues from becoming major failures. For multi-battery systems, voltage imbalance is a common concern. Proactive checks are simple and highly effective.
- Use a Battery Monitor: Install a monitor with a shunt (like a Victron BMV or SmartShunt) for precise SOC tracking beyond just voltage.
- Check Individual Cell Voltages: For DIY battery banks, periodically measure each cell’s voltage with a multimeter. A variance greater than 0.1V may indicate a need for balancing.
- Perform Top Balancing: If cells are imbalanced, a controlled top balance at the full charge voltage can synchronize them. Always follow safety guidelines.
Maintenance Checklist:
- Monthly: Verify system charging voltages match settings.
- Quarterly: Check voltage of individual batteries/cells in a bank.
- Annually: Inspect terminals for corrosion and ensure tight connections.
Troubleshooting Common LiFePO4 Voltage Issues
Even with proper care, you may encounter voltage-related problems. This section helps diagnose and resolve the most common issues. Quick identification prevents performance loss and potential damage.
Battery Not Holding Charge (Voltage Drops Quickly)
A rapid voltage drop under load or at rest indicates a problem. This symptom often points to capacity loss or a system issue. Follow this diagnostic sequence to find the root cause.
- Check for Parasitic Load: Use a clamp meter to detect small, constant drains from systems like alarms or inverters in standby mode.
- Test Under Load: Measure voltage during a known discharge. If it plunges immediately, the battery may have a weak or damaged cell.
- Verify Charging Cycle: Ensure your charger is actually reaching the full absorption voltage. A faulty charger or undersized solar array can cause chronic undercharging.
Voltage Sag and Surface Charge
It’s crucial to distinguish between normal voltage behavior and actual faults. Two common phenomena are voltage sag and surface charge. Misinterpreting these can lead to unnecessary concern.
- Voltage Sag: This is a normal, temporary drop in voltage when a high load is applied (e.g., starting an inverter). The voltage should recover once the load is removed if the battery is healthy.
- Surface Charge: A higher voltage reading immediately after charging ends. For an accurate SOC reading, let the battery “rest” for 1-2 hours with no charge or load before measuring.
- Persistent Low Voltage: If voltage remains low after resting and a full charge attempt, it may indicate a failed BMS, severely unbalanced cells, or age-related capacity fade.
Quick Reference: Voltage Problem & Probable Cause
Symptom: Voltage reads 13V+ but drops fast under small load.
Likely Cause: Surface charge. Let battery rest before testing.
Symptom: Battery won’t charge above 13V (12V system).
Likely Cause: Charger set incorrectly, faulty BMS, or cell imbalance.
LiFePO4 vs. Other Battery Chemistries: Voltage Comparison
Choosing the right battery requires understanding key differences in voltage behavior. LiFePO4 offers a distinct profile compared to lead-acid and other lithium types. This comparison highlights why voltage settings are not interchangeable.
Voltage Profile: LiFePO4 vs. Lead-Acid
The discharge curve is the most significant practical difference. Lead-acid batteries have a steep, sloping voltage drop as they discharge. LiFePO4 maintains a much flatter voltage plateau for most of its capacity.
| Characteristic | 12V LiFePO4 | 12V Flooded Lead-Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 12.8V | 12.0V |
| Full Charge Voltage | ~14.4V | ~12.6V – 12.8V (Resting) |
| Usable Voltage Range | 13.4V – 12.8V (Flat) | Steady decline from 12.8V to 11.8V |
| 50% SOC Voltage | ~13.1V | ~12.1V |
| Key Advantage | Consistent power output | Wider voltage indicates SOC |
Why You Cannot Use Lead-Acid Charger Settings
Using a charger programmed for lead-acid can severely damage a LiFePO4 battery. The voltage requirements and charging algorithms are fundamentally different. This is a critical safety and longevity consideration.
- Overcharging Risk: Lead-acid chargers may apply a higher equalization voltage (15V+), which is dangerous for LiFePO4 and can cause a fire hazard.
- Undercharging Issue: They may also use a lower absorption voltage, failing to fully charge the lithium battery and leading to chronic undercapacity.
- Solution: Always use a charger with a dedicated LiFePO4 or user-programmable profile. Never assume compatibility based on voltage alone.
Critical Warning: The Battery Management System (BMS) is your last line of defense. However, never rely solely on the BMS to correct for a poorly configured charger. Always set your source equipment (charger, solar controller) to the correct LiFePO4 voltage parameters first.
Advanced LiFePO4 Voltage Topics and Safety
For users designing custom systems or pushing performance limits, deeper knowledge is essential. These advanced topics cover cell-level management and critical safety protocols. Understanding these principles ensures robust and safe system operation.
Cell-Level Voltage and Battery Management Systems (BMS)
A LiFePO4 battery is made of multiple 3.2V nominal cells in series. The BMS is the brain that monitors and protects each cell individually. Its primary voltage-related functions are crucial for safety.
- Cell Balancing: The BMS passively or actively balances cell voltages to prevent any single cell from overcharging or over-discharging, which extends pack life.
- Over/Under Voltage Protection: It disconnects the battery if any cell exceeds safe limits (typically ~3.65V max, ~2.5V min).
- Communication: Smart BMS units provide cell voltage data via Bluetooth or CAN bus, allowing for precise diagnostics.
Critical Safety Protocols for High-Voltage Packs
24V and 48V systems operate at potentially lethal DC voltages. Proper handling and installation are non-negotiable. Always prioritize safety over convenience when working with these systems.
- Always Disconnect Power: Before working on any part of the system, disconnect both the charge source and the load. Verify no voltage is present with a multimeter.
- Use Proper Fusing and Breakers: Install a Class T fuse or appropriate DC breaker on the positive terminal, as close to the battery as possible, to interrupt fault currents.
- Implement a System Disconnect: Use a manual disconnect switch to isolate the battery bank for maintenance and emergencies. Ensure all wiring is rated for the maximum system amperage.
Safety First: Pre-Installation Checklist
- ✅ Wear insulated gloves and safety glasses.
- ✅ Use tools with insulated handles.
- ✅ Ensure all connections are tight and corrosion-free.
- ✅ Install batteries in a ventilated, fire-resistant enclosure.
- ✅ Keep a Class D fire extinguisher accessible.
Essential Tools for Monitoring LiFePO4 Battery Voltage
Accurate monitoring requires the right tools. Guessing your battery’s state of charge is inefficient and risky. Investing in proper equipment pays for itself through improved performance and longevity.
Must-Have Tools for Every Owner
These basic tools are essential for routine checks and troubleshooting. They provide a direct, reliable way to measure your system’s health. Every LiFePO4 owner should have them in their toolkit.
- Digital Multimeter (DMM): A fundamental tool for measuring voltage at the battery terminals, busbars, and individual cells. Look for a true RMS model for accuracy.
- Battery Monitor with Shunt: Devices like the Victron BMV-712 or SmartShunt track amp-hours in/out, providing the most accurate SOC reading, independent of voltage.
- Infrared Thermometer: Useful for spotting hot connections or cells, which can indicate high resistance, poor connections, or internal problems.
Choosing and Using a Battery Monitor
A dedicated battery monitor is the single best upgrade for managing a LiFePO4 system. It moves you from guessing to knowing. Proper setup is key to reaping its benefits.
- Select the Right Capacity: Choose a monitor whose shunt is rated for your system’s maximum continuous current, plus a 20% safety margin.
- Program Correct Parameters: Input your battery’s exact amp-hour (Ah) capacity and set the correct charge voltage thresholds for synchronization.
- Install the Shunt Properly: Mount the shunt on the negative terminal, with all loads and charge sources connected to the load side. The battery connects to the other side.
Tool Comparison: Multimeter vs. Battery Monitor
Digital Multimeter: Best for spot-checking static voltage, diagnosing no-power issues, and measuring cell-level voltage. It gives a momentary snapshot.
Battery Monitor (Shunt): Essential for tracking dynamic SOC, total energy consumed, and long-term trends. It provides continuous, contextual data.
Conclusion: Mastering Your LiFePO4 Battery Voltage
Understanding your LiFePO4 battery’s voltage profile is fundamental to its performance and lifespan. This guide provides the essential charts and knowledge for 12V, 24V, and 48V systems. Proper voltage management ensures reliable power and maximizes your investment.
The key takeaway is to use the correct charger settings and monitor voltage with the right tools. Never rely on lead-acid profiles. Pair your battery with a compatible smart charger and a quality battery monitor.
Bookmark this page and refer to the voltage charts during system setup or troubleshooting. Share this guide with others who rely on lithium power. Your next step is to check your current system settings against our recommended parameters.
With this knowledge, you can confidently maintain your LiFePO4 battery for years of optimal service. Enjoy the peace of mind that comes with truly understanding your power system.
Frequently Asked Questions about LiFePO4 Battery Voltage
What is the resting voltage of a fully charged 12V LiFePO4 battery?
A fully charged 12V LiFePO4 battery at rest (after 1-2 hours) will read approximately 13.3 to 13.4 volts. This is different from the charging voltage. The higher 14.2V-14.6V seen during charging is the absorption voltage, which will taper down once the battery is full.
This resting voltage is your most accurate indicator of a 100% state of charge. Always measure voltage after disconnecting charge sources and loads for a short period to get a true reading.
How do I check the state of charge on my LiFePO4 battery?
The best method is to use a battery monitor with a shunt that tracks amp-hours. This provides the most accurate SOC percentage. If using voltage alone, refer to the resting voltage chart in this guide and ensure the battery is not under load or recently charged.
For a quick estimate, a resting voltage of 13.3V means ~100%, 13.0V is ~40%, and 12.7V is ~20% SOC. Remember, voltage under load (voltage sag) is not an accurate SOC indicator.
What voltage should I set my LiFePO4 charger to?
For a 12V system, set your absorption/bulk voltage to 14.2V to 14.6V, as specified by your battery’s manufacturer. The float voltage should be set between 13.5V and 13.8V if used. Many modern chargers have a dedicated LiFePO4 profile that automatically selects these parameters.
It is critical to never use a lead-acid charger profile, as the higher equalization voltages can be dangerous and will damage your lithium battery over time.
Why does my LiFePO4 battery voltage drop so fast under load?
This is typically normal voltage sag, a temporary drop when a high-current load engages. The voltage should recover once the load is removed if the battery is healthy. If the voltage stays low, it may indicate a weak cell, a poor connection, or the battery is actually at a low state of charge.
First, check the resting voltage after the load is removed. If it remains abnormally low, investigate connections and consider testing individual cell voltages if possible.
What is the lowest safe voltage for a 12V LiFePO4 battery?
The low voltage disconnect (LVD) for a 12V LiFePO4 is typically around 12.0V (2.5V per cell). Discharging below this point stresses the battery and can cause permanent damage. Most Battery Management Systems (BMS) will cut off power to protect the cells at this threshold.
For longevity, it’s best practice to set your inverter or system LVD slightly higher, around 12.2V, to provide a safety buffer and avoid triggering the BMS cutoff.
Can I use a lead-acid battery voltage chart for my LiFePO4?
No, you cannot use a lead-acid voltage chart. The voltage profiles and state-of-charge correlations are completely different. A LiFePO4 battery spends most of its discharge cycle between 13.3V and 12.8V, while a lead-acid battery steadily declines from 12.8V down.
Using the wrong chart will give you highly inaccurate SOC readings. Always refer to a LiFePO4-specific voltage chart, like the one provided in this article.
How does temperature affect LiFePO4 battery voltage?
Temperature has a minor effect on voltage readings but a major effect on charging safety. Voltage readings may be slightly lower in cold temperatures. Crucially, you must not charge a LiFePO4 battery below 32°F (0°C) without a temperature-compensated charger.
Charging a frozen battery can cause permanent lithium plating on the anode, reducing capacity and creating a safety risk. Many BMS units include low-temperature charging lockout for protection.
What does it mean if my battery cells have different voltages?
Different cell voltages indicate an imbalance within the battery pack. A small variance (0.1V or less) is normal, but larger gaps reduce capacity and strain the BMS. The BMS works to balance cells, but severe imbalance may require a manual top balance.
For DIY battery banks, periodic cell voltage checks are good maintenance. For sealed commercial batteries, significant imbalance may require contacting the manufacturer, as it can signal a failing cell.
